Fiber Optic Connector - Definition, Types and Uses
 Published: Apr 25, 2023
Published: Apr 25, 2023
Contents
What is Fiber Optic Connector?
The fiber optic connector is a removable (movable) connection between the fiber and the fiber device, and it is the two ends of the fiber precision butt to enable the launch of the optical fiber output light energy to maximize coupling to the receiving fiber and make its intervention in the optical link to minimize the impact on the system, which is the basic requirements of the fiber optic connector. To a certain extent, the fiber optic connector affects the reliability and performance of the optical transmission system.
Types of Fiber Optic Connectors
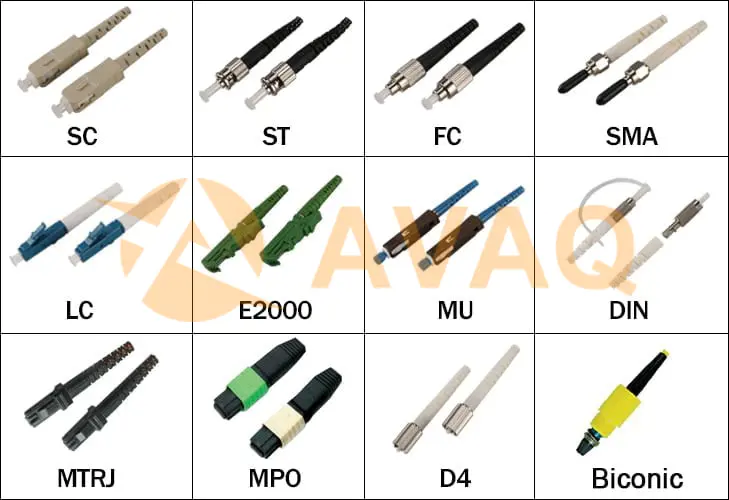
Fiber optic connectors, according to the different transmission media, can be divided into common silicon-based fiber single-mode and multimode connectors, and other such as plastic as the transmission medium of fiber optic connectors; according to the connector, structure form can be divided into: FC, SC, ST, LC, D4, DIN, MU, MT and so on various forms. Among them, ST connectors are usually used for cabling equipment, such as fiber optic patch panels, fiber modules, etc.; while SC and MT connectors are usually used for network equipment. According to the shape of the fiber endpoints FC, PC (including SPC or UPC), and APC, according to the number of fiber cores divided into single-core and multi-core (such as MT-RJ) points. Fiber optic connectors are widely used in a wide variety of ways. In the actual application process, we generally follow the different structures of fiber optic connectors to distinguish. The following are some common fiber optic connectors:
FC-Type Fiber Optic Connectors
FC is the abbreviation of Ferrule Connector, indicating that its external reinforcement is the use of metal sleeves, a fastening method for the screw buckle. The earliest FC-type connector, using ceramic pins of the docking end face, is a flat contact method (FC). This type of connector structure is simple, easy to operate, and easy to make, but the fiber end face is more sensitive to dust and easy to produce Fresnel reflection, improving the return loss performance is more difficult. Later, the type of connector was improved, using the butt end face as a spherical pin (PC), while the external structure has not changed, making the insertion loss and return loss performance has been improved significantly.
SC-Type Fiber Optic Connectors
Its shell is rectangular, and the structure of the pins and coupling sleeve dimensions are identical to the FC type. The end face of the pins is mostly ground in PC or APC type; the fastening method is to use the plug and pin latch type without rotation. Such connectors are inexpensive, easy to plug and unplug operation, small fluctuations in intervention loss, high compressive strength, and high installation density.
ST and SC interface are two types of fiber optic connectors. For the 10Base-F connection, the connector is usually ST type; for 100Base-FX, the connector is SC type in most cases. The core of the ST connector is exposed, and the core of the SC connector is inside the connector.
Biconic Connector
DIN47256 type fiber optic connector This is a connector developed by Germany. This connector uses the same structural dimensions of the pin and coupling sleeve as the FC type, and the end face is treated by PC grinding. Compared with the FC-type connector, its structure is more complex, and the internal metal structure has a spring to control the pressure, which can avoid damage to the end face due to excessive plugging pressure. In addition, the mechanical accuracy of this connector is higher, so the intervention loss value is smaller.
MT-RJ Type Connectors
MT-RJ started from the MT connector developed by NTT, with the same latching mechanism as the RJ-45 type LAN electrical connector, and is aligned with the optical fiber by the guide pins mounted on both sides of the small sleeve.
LC Type Connector
LC type connector is the famous Bell (Bell) Research Institute research and development, the use of easy to operate modular jack (RJ) latch mechanism made. The size of the pins and sleeves used is half the size of the common SC, FC, etc., at 1.25 mm, which can increase the density of fiber optic connectors in the fiber optic distribution frame. Currently, in single-mode SFF, LC-type connectors have actually dominated, and the application in multimode is also growing rapidly.
MU Type Connectors
MU (Miniature unit Coupling) connector is the world's smallest single-core fiber optic connector developed by NTT based on the most used SC type connector. This connector uses a 1.25mm diameter sleeve and self-retaining mechanism and has the advantage of high-density installation. Using the MU's l.25mm diameter sleeve, NTT has developed the MU connector series. They are socket-type connectors for fiber optic cable connections (MU-A series), baseboard connectors with self-retaining mechanisms (MU-B series), and simplified sockets for connecting LD/PD modules to plugs (MU-SR series). With the rapid development of fiber optic networks toward larger bandwidth and larger capacity and the widespread use of DWDM technology, the demand for MU-type connectors will also grow rapidly.
MC Connectors
MC fiber optic movable connector is a high-density single-core fiber optic movable connector suitable for various high-density applications, such as high-capacity central server rooms and high-density data centers. MC fiber optic movable connector has high density, up to twice as high as LC connector in the same space, which is the smallest and highest density connector in the world.
General Construction
The main purpose of fiber optic connectors is used to realize the splicing of optical fibers. Fiber optic connectors have been widely used in fiber optic communication systems, and there are many different types of connectors with different structures. However, in detail, the basic structure of various types of fiber optic connectors is the same; that is, the majority of fiber optic connectors generally use high-precision components (consisting of two pins and a coupling tube of three parts) to achieve the alignment of the fiber connection.
In this method, the optical fiber is inserted and fixed in the pins, and the surface of the pins is polished and aligned in the coupling tube. The outer component of the pin is made of metallic or non-metallic material. The butt end of the pin must be polished, and the other end is usually made with a bend-limiting member to support the fiber or fiber flexible cable to relieve stress. The coupling tube is generally made of ceramic, bronze, and other materials, and the two halves of the composite, fastened cylindrical components are made, more often with metal or plastic flange, to facilitate the installation of the fixed connector. In order to align the fiber as accurately as possible, the processing accuracy of the pin and the coupling tube is very high.
Performance
(1) optical performance
The optical performance requirements for fiber optic connectors, mainly insertion loss and return loss, are the two most basic parameters.
Insertion loss (insertion loss), that is, the connection loss, is the loss of effective optical power of the link caused by the introduction of the connector. The smaller the insertion loss, the better; the general requirement should not be greater than 0.5 dB.
Return loss (ReturnLoss, ReflectionLoss) refers to the connector on the optical link power reflection suppression ability; its typical value should not be less than 25dB. The practical application of the connector, the pin surface after a special polishing process, can make the return loss greater, generally not less than 45dB.
(2) Interchangeability, repeatability
Fiber optic connectors are universal passive devices for the same type of fiber optic connectors, generally can be used in any combination, and can be used repeatedly, which is generally less than 0.2dB of additional loss into the range.
(3) Tensile strength
For a good fiber optic connector, the general requirements of its tensile strength should not be less than 90N.
(4) Temperature
General requirements, fiber optic connectors must be in the -40oC ~ +70oC temperature range and can be used normally.
(5) plugging and unplugging times
The use of fiber optic connectors can basically plug and unplug more than l000 times.
Connection Steps
1, fiber optic quick connector is a very innovative field termination connector, which contains factory pre-assembled fiber, pre-polished ceramic insert, and a mechanical splicing mechanism.
2, when terminated, simply insert the incoming fiber or indoor fiber into the mechanical splicing mechanism without the use of other tools; the termination process takes only about 2 minutes, greatly saving installation time.
3, fiber optic quick connectors inside the core and end face are factory pre-milled and pre-polished, mechanical splicing mechanism is located at the end of the core, used to fix the inserted fiber.
4, the mechanical splicing mechanism mainly consists of V-groove and clamping elements; when the fiber needs to be inserted, open the V-groove with a wedge-shaped clip to facilitate the smooth insertion of optical fiber.
5, When the fiber is inserted into the V-slot and fixed, the wedge clip can be pulled out from the V-slot.
 Popular Industry Focus
Popular Industry Focus
Hot Products
-
![HCEM100DUE8P5]()
HCEM100DUE8P5
TE Connectivity
Board Mount Pressure Sensors HCEM100DUE8P5;PRES;0...100mbard;5V;SMD
-
![D5601-001205-050PD]()
D5601-001205-050PD
TE Connectivity
Industrial Pressure Sensors PRESS XDCR D5601-001205-050PD
-
![LL10-1AD04]()
LL10-1AD04
TE Connectivity
Liquid Level Sensors LL10 4FT CABLE 6"AP 80C
-
![FS1901-0000-1000-G]()
FS1901-0000-1000-G
TE Connectivity
1000 GRAM FORCE 20MV/V FORCE LOAD CELL
-
![HPP845E034R4]()
HPP845E034R4
TE Connectivity
Humidity, Temperature 0 ~ 100% RH I²C ±5% RH 5 s Surface Mount
-
![HMAM250UU7H5]()
HMAM250UU7H5
TE Connectivity
Board Mount Pressure Sensors HMAM250UU7H5;PRES;0-250mbar;4V;5V


 Update Time: Apr 25, 2023 Consumer Electronics
Update Time: Apr 25, 2023 Consumer Electronics